Category: Anwendungen & Problemlösungen
- März 2021
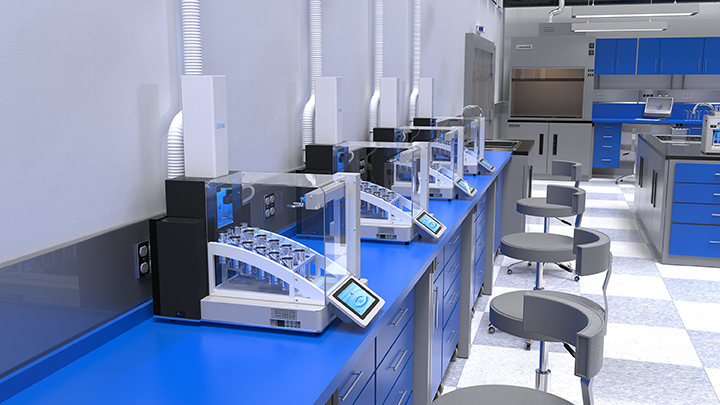
Für die Lebensmittel- und Bedarfsgegenstände-Analytik (§ 64 LFGB) und die Umweltanalytik sind schnelle, leistungsfähige und innovative Aufschlussverfahren von entscheidender Bedeutung. Das Aufschlussverfahren muss auf die nachfolgende Analytik der Hydrid-/Kaltdampf-/Flammen- oder Graphitofen-AAS, ICP-OES bzw. ICP-MS abgestimmt sein.
Im Rahmen dieses Web-Seminars erläutern Ihnen die Referenten Frank Scholten und Ulf Sengutta die modernen Mikrowellen-Aufschlussmethoden von wenigen Milligramm Einwaage bis hin zu mehreren Gramm bzw. Millilitter. Einwaage.
Lösemittel-Extraktionen im MARS und EDGE
Soils and river sediments were frozen and freezedried at ETH Zürich. Soils were sieved, and the fraction <2 mm was used for further analysis. Analytical techniques for brGDGT analyses follow Hopmans et al. (2016) and Freymond et al. (2017) and are summarized here with a detailed description in the supporting information. Briey, between 2 and 3 g of the soil samples and around 20 g of the river sediments were
extracted with solvents in a microwave or an automated extraction system. After purification via column chromatography and preltration, the GDGT distributions were analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (HPLC MS) at ETH Zürich.
10. März 2021, ab 10.15 Uhr
Erleben Sie einen ganzen Tag interessante Vorträge zu den Neuigkeiten der Peptid-Synthese. Aufgrund der Corona-Situation können Präsenzvorträge derzeit nicht stattfinden. Deshalb veranstaltet CEM zusammen mit bekannten Forschern/innen dieses kostenfreie Online Seminar.
Academic Guest Speakers:
Professor Anna Maria Papini
University of Florence,
CY Cergy Paris Université

The challenge to design fully automated solid-phase MW-assisted cGMP ready processes of peptide production as active pharmaceutical ingredients
Interdepartmental Research Unit of Peptide & Protein Chemistry and Biology, Departments of Chemistry and NeuroFarBa, University of Florence (Italy)
With the increase of approved peptide-based drugs and patents expiring, the manufacturers’ need in production of peptides is dramatically rising. Companies involved in peptide-based drugs that have to be compliant with good manufacturing practices (GMP), face several challenges, such as high production costs on downstream processes (due to the use of high raw material amounts) and bad scalability. Therefore, the main challenge of production of active peptides as pharmaceutical ingredients is to find solutions to specific problems encountered during scale-up.
As a proof-of concept we will report the strategies we investigated for the preparation of Eptifibatide, scalable to kilogram-scale, having in common the use of the microwave-assisted solid-phase peptide synthesis (MW-SPPS) procedure, which is now available not only at R&D level but also for the large-scale manufacturing of peptides. Following the very fast microwave-assisted Fmoc/tBu synthesis of the Eptifibatide linear precursor by a DIC/Oxyma Pure coupling protocol at 90 °C, we explored both the solution (off-resin) and the solid-phase (on-resin) disulfide bond formation.
The relevance of the strategy we optimized is essentially based on the selection of the StBu orthogonal protection on cysteine that is easily removed by MPA acting as a novel reducing agent for Cys(StBu) deprotection. Moreover, we demonstrated that all operations can be performed by fully automated process in the instrumentation.
To the best of our knowledge, this is a unique strategy performing all the processes including disulfide bond formation in a single reactor and represents an optimized scalable fully automated solid-phase microwave-assisted cGMP-ready process to prepare Eptifibatide.
Designing Synthetic Peptides to Explore the Dark Matter of Protein Space
Dek Woolfson
Schools of Chemistry and Biochemistry, & Bristol BioDesign Institute
University of Bristol, UK
Protein design—i.e., the construction of entirely new protein sequences that fold into prescribed structures—has come of age: it is now possible to generate a wide variety stable protein folds from scratch using rational and/or computational approaches. A new challenge for the field is to move past protein structures offered up by nature and to target the so-called ‘dark matter of protein space’; that is, protein structures that should be possible in terms of chemistry and physics, but which biology seems to have overlook or not used prolifically. This talk will illustrate what is currently possible in this nascent field using de novo a-helical coiled-coil peptides as building blocks for assembling larger, more-complex and functional protein-like structures.1
Coiled coils are bundles of 2 or more a helices that wrap around each other to form rope-like structures. They are one of the dominant structures that direct natural protein-protein interactions. Our understanding of coiled coils provides a strong basis for building new proteins from first principles. The first part of my talk will survey this understanding,1 our design methods,2,3 and our current “toolkit” of de novo coiled coils.4-5
Next, I will describe how the toolkit can be expanded used to generate some dark-matter protein structures. I’ll focus on the rational and computational design of a-helical barrel proteins, which have 5 or more helices surrounding accessible central channels.6 Finally, I’ll discuss how these synthetic barrel proteins can be put to use to make new nanotube materials,7 rudimentary catalysts,8 membrane-spanning pores,9 and the components of a new types of sensing devices.10
Professor Dek Woolfson
University of Bristol

Professor Fernando Albericio
University of Barcelona,
University of Kwazulu-Natal

Microwave-Assisted Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis, A Unique Tool for Peptide Research
Fernando Albericio,1,2 Beatriz G. de la Torre1
1University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban 4001, South Africa; 2University of Barcelona, 08028-Barcelona, Spain
During the last five years (2016-2020), 18 drugs containing peptides have been approved by the US FDA. In addition, several hundred are in clinical phases or advanced preclinical studies. The development of new synthetic strategies has facilitated this explosion in the world of peptides. In this regard, the development of new resins, coupling reagents, protecting groups, and, more importantly, reliable and robust peptide synthesizers have been vital for the consolidation of the peptide drug market.
In the field of automatic synthesizers, the last breakthrough occurred when at the beginning of this century, CEM launched the new concept of Microwave-Assisted SPPS. Our group and others have demonstrated that both couplings and Fmoc-removal are better performed in the microwave mode compared with classical synthesis or even with conventional heating. More important, this better performance in the two key reactions is not accompanied by any significant side-reaction.
This presentation will discuss our last results on the use of Microwave synthesis for the preparation of intriguing peptides and/or for developing new synthetic strategies: (i) the preparation of staple peptides via late-stage C(sp2)-H Pd activation using the microwave; (ii) synthesis of N-alkyl amino acid containing peptides; (iii) development of new and more efficient coupling reagents; and (iv) microwave-based Green Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (GSPPS).
In the GSPPS, the CEM Liberty Blue Microwave technology by itself could be considered green in terms of solvent consumption and time-saving and due to the excellent quality of the crude peptides, which enormously facilitates the purification with the consequent increase of yield and reduction of chromatography solvents.
Short antimicrobial peptides – discovery and optimization
Kai Hilpert, St George’s University
The global health threat surrounding bacterial resistance has resulted in antibiotic researchers shifting their focus away from ‘traditional’ antibiotics and concentrating on other antimicrobial agents, including antimicrobial peptides.
These peptides exhibit broad-spectrum activity against bacteria, including multi-drug resistant strains, viruses, fungi, and protozoa, and constitute a major element of the innate immune system of many multicellular organisms.
We use the Spot-synthesis technique to study and optimize naturally occurring as well as artificial antimicrobial peptides. Understanding the features that make them antibacterial and hemolytic allows for targeted drug development.
Extraktion mit dem MARS und EDGE:
Lipids were extracted from dried soil samples using a microwave (CEM MARS5) or an Energized Dispersive Guided Extraction (CEM EDGE) system. No difference in performance was observed for the different extraction systems. Samples were processed in batches of roughly 15 to 20 g of material. For microwave extraction the samples were transferred to the extraction vessels and covered by a dichloromethane (DCM):methanol (MeOH) 9:1 (v/v, 25 ml) solvent mixture. Extraction temperature was programmed to ramp to 100 ◦C in 35 min and is subsequently held for 20 min. For EDGE extraction 25 ml DCM:MeOH 9:1105 (v/v) was used for extraction at 110 ◦C for 2 min and subsequent rinsing with 15 ml followed by a second extraction with 5 ml of solvent at100 ◦C and rinsing with35ml. The process was repeated on additional samplebatches to yield sufficient quantities of the target lipid compounds for 14C analysis. Pooled extracts were then dried under nitrogen flow.
4. März 2021
Der Verdauautomat DigestPro stellt eine kompakte Lösung zur Automatisierung von Proteinverdaumethoden (In-Gel & in Lösung) dar, wodurch der Probendurchsatz erhöht und ein kontaminationsfreies Arbeiten garantiert wird. Bis zu 96 Proben können simultan verdaut werden. Auch eine nachfolgende Proben-Aufreinigung und die Überführung in Autosampler-Vials oder das Spotten auf MALDI-Targets ist möglich. Durch den modularen Aufbau lässt sich das Gerät optimal an individuelle Anforderungen anpassen. Die Verwendung laboreigener Reagenzien minimiert die laufenden Kosten. Vorinstallierte Standardprotokolle lassen sich sehr einfach modifizieren und auch anwenderspezifische, neue Methoden können programmiert werden.
Im Rahmen dieses Web-Seminars erläutert Ihnen der Referent Dr. Martin Technau live die einfache und sichere Handhabung des DigestPro für den vollautomatischen Proteinverdau und nachfolgende Methoden zur MS-Probenvorbereitung. Zudem können per Chat individuelle Fragen gestellt werden.
Um Ihnen die Terminplanung zu erleichtern, bieten wir das Web-Seminar am Donnerstag, den 4. März 2021 zu zwei verschiedenen Uhrzeiten an: 10.00 Uhr und 14.00 Uhr (Dauer: ca. 1 Stunde)
Melden Sie sich hier zum kostenfreien Web-Seminar an
Peptid-Synthese im Liberty Blue
The insulin-like peptide human relaxin-2 was identified as a hormone that, among other biological functions, mediates the hemodynamic changes occurring during pregnancy. Recombinant relaxin-2 (serelaxin) has shown beneficial effects in acute heart failure, but its full therapeutic potential has been hampered by its short half-life and the need for intravenous administration limiting its use to intensive care units. In this study, we report the development of long-acting potent single-chain relaxin peptide mimetics. Modifications in the B-chain of relaxin, such as the introduction of specific mutations and the trimming of the sequence to an optimal size, resulted in potent, structurally simplified peptide agonists of the relaxin receptor Relaxin Family Peptide Receptor 1 (RXFP1) (e.g., 54). Introduction of suitable spacers and fatty acids led to the identification of single-chain lipidated peptide agonists of RXFP1, with sub-nanomolar activity, high subcutaneous bioavailability, extended half-lives, and in vivo efficacy (e.g., 64).
Die Autoren stellen eine neue Labormethode vor, die das ideale Zusammenspiel von Probenvorbereitung inkl. Zerkleinern und Homogenisieren mit geeigneten Labormühlen für die Fettanalytik beschreibt.
Gerade heterogene Lebensmittel mit Füllungen wie z. B. Kartoffeltaschen mit Frischkäse, Frühlingsrollen mit Gemüse und Fleisch, vegetarische Schnitzel mit Panade, Tortellini mit Fleischfüllung, Speck mit Fettkante und magerem Fleisch, Mettwürstchen mit Pfefferkörnchen und Fettkügelchen sowie Pizza mit unterschiedlichen Belägen stellen hohe Anforderungen an die Zerkleinerung und Homogenisierung der Proben. Die Präzision und Richtigkeit der Fettgehalte steht in direktem Zusammenhang zur vorgeschalteten Probenvorbereitung.
#Fachberichte #Whitepaper #Lebensmittel #Fettgehalt
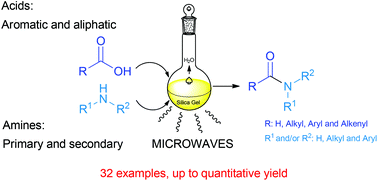
A highly improved and green methodology for the direct amidation of carboxylic acids with amines using silica gel as a solid support and catalyst is described. The scope of this method is exemplified by the use of several aliphatic, aromatic, unsaturated and fatty acids. The reaction is also applied to different primary and secondary amines. Typically, the amines should be aliphatic, but aromatic amines can be used as well, though with lower yields. Several experiments to illustrate the selectivity of this methodology were also carried out with several more functionalized acids and amines. This approach is a substantial improvement over other previously described methods in amide synthesis.
Amine (1.5 mmol) and carboxylic acid (1.5 mmol) were dissolved in ethyl acetate (15 mL), then silica gel 60 230-400 mesh (1.0 g) was added. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, the reactant mixture was transferred to a microwaves tube, and it was set to react in a CEM microwave reactor in cycles of 20 minutes at a power of 200 W maintaining constant temperature at 130 °C, and a hold time of 2 minutes. The reactant mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, sonicated for 20 minutes with 30 mL of ethyl acetate, filtered, and the silica was washed with another 30 mL of ethyl acetate. The organic phase was washed with a saturated solution of NaHCO3 and HCl (10%), dried over MgSO4, filtered and the solvent was withdrawn under reduced pressure to obtain the pure product. In some cases flash chromatography was and it is indicated in the characterization data.
Mittwoch, 24. Februar 2021
Für die Lebensmittel-Analytik und verwandte Branchen sind schnelle, korrekte und präzise Messungen von Feuchte, Fett und Eiweiß von entscheidender Bedeutung.
Im Rahmen dieses Web-Seminars erläutern Ihnen die Referenten Frank Scholten und Ulf Sengutta die modernen Analysenmethoden zum schnellen, sicheren und einfachen Arbeiten am Smart 6, Oracle und Sprint für die unterschiedlichsten Anwendungsgebiete:
- Molkereiprodukte, Fleisch- und Wurstwaren, Saucen/Dressings, Senf, Mayonnaise, Eiscreme, Schokolade, Plant Based Materials (Soja, Reis, Hafer, Kokos, Mandeln), Eiprodukte, Snacks, Butter, Kaffee, Proben mit Lufteinschlüssen wie Kefir und geschäumten Puddings, komplexe Proben (Kartoffeltaschen mit Frischkäse, Frühlingsrollen, Pizza, Fertiggerichte)
- Für die Prozesskontrolle von warmen Proben wie Schmelzkäsezubereitungen, angemischten inhomogenen Proben ist diese Methode ebenfalls gut geeignet.
- Geeignet für schnelle Eingangs-, Prozess-, Endprodukt-Kontrolle
- Auftragslaboratorien – Hoher Probendurchsatz/Automatisierung ist möglich
- Tierfutter, Futtermittel, Fettabscheider, Biomasse, Naturstoffe (Oliven…),
In praktischen Übungen werden live Proben bearbeitet. Und zudem können per Chat individuelle Fragen gestellt werden. Es besteht die Möglichkeit der Bearbeitung von Kundenproben nach dem Web-Seminar.
Um die Terminplanung zu erleichtern, bieten wir das Web-Seminar am Mittwoch, den 24. Februar 2021 zu zwei verschiedenen Uhrzeiten an:
10.00 Uhr und 14.30 Uhr (Dauer: ca. 1 Stunde)
Hier erfolgt die kostenfreie Anmeldung
Mittwoch, 24.2.2021 um 14.00 Uhr
Soil is one of the most common matrices in which semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) are present. The extraction of these compounds from soil can be a lengthy and tedious process. Pressurized Fluid Extraction on the EDGE and Microwave Assisted Solvent Extraction (MASE) on the MARS 6 are proven techniques that are fast, simple, and efficient. EDGE is ideal for difficult samples while MARS 6 is ideal for high throughput labs dealing with hundreds of samples per day. Adhering to US EPA 3545A the EDGE offers a rapid automated process that yields a filtered sample. Adhering to US EPA 3546, the MARS 6 also offers an efficient extraction of up to 24 samples simultaneously. These two techniques offers solutions for rapid, simple and efficient extraction of SVOCs from soil. Join CEM’s Benedict Liu and Alicia Douglas Stell, PhD as they compare two methods for extraction of SVOCs from soil and discuss how each system can benefit your lab.
Registrieren Sie sich und nehmen Sie an der Live-Fragerunde teil