Tag: Extraktion
Highlights
-
•Validated and time-efficient enzymatic-oxidative sample preparation
-
•Microplastic analysis based on LDIR/quantum cascade laser IR imaging
-
•Volume-reduced sampling via fractionated filtration system
-
•First large scale report of microplastic concentrations in the tropical Indian Ocean
#Analytik #Mikroplastik #Probenvorbereitung #Mikrowellenaufschluss #microwavedigestion #mikrowellenreaktionstechnik #CEM #Umweltanalytik
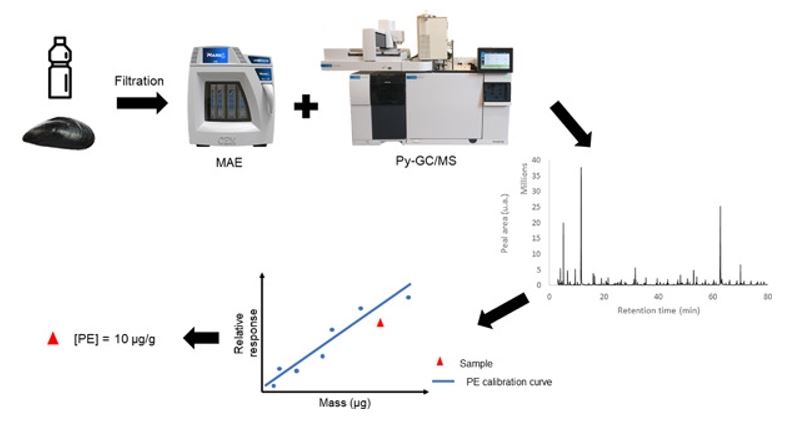
Microwave-Assisted Extraction for Quantification of Microplastics Using Pyrolysis–Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
Mars 6 zur Lösemittel-Extraktion:
Microplastics (MP) are now recognized as a persistent and global pollutant. To quantitively measure MPs in environmental matrices, several techniques are used – including new methods using Pyrolysis‐Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. In this study, a new extraction method using Microwave‐Assisted Extraction (MAE) combined with Py‐GC/MS was developed to extract and quantify a wide range of plastic polymers and validated using different environmental matrices.
Gummigranulate werden auf Kunstrasenplätzen als Füllmaterial verwendet. In loser Form werden Granulate und Mulche aus Gummi zudem auf Spielplätzen oder im Sportbereich verwendet, etwa auf Golfplätzen, auf Leichtathletikanlagen, in Böden von Pferdesportanlagen, auf Wanderwegen oder in Schießständen. Die betreffenden Granulate und Mulche werden überwiegend aus Altreifen gewonnen. Einer der Hauptgründe für die Bedenken hinsichtlich der Verwendung von aus Altreifen gewonnenen Granulaten und Mulchen ist das Vorhandensein der acht PAK in der Matrix des Gummis.
aus:
Verordnung (EU) 2021/1199 der Kommission vom 20. Juli 2021 zur Änderung von Anhang XVII der Verordnung (EG) Nr. 1907/2006 des Europäischen Parlaments und des Rates in Bezug auf polyzyklische aromatische Kohlenwasserstoffe (PAK) in Granulaten oder Mulchen zur Verwendung als Füllmaterial auf Kunstrasenplätzen oder in loser Form auf Spielplätzen oder im Sportbereich
Entdecken Sie die Vorteile der EDGE-Lösemittelextraktion versus ASE-Methode und wie Sie dadurch viel Zeit sparen, Ihren Probendurchsatz erhöhen und Geld sparen können.
„Comparison of Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE) and Energized Dispersive Guided Extraction (EDGE) for the analysis of pesticides in leaves“
Zusammenfassung
- •An Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE) method for 20 pesticides was developed.
- •An Energized Dispersive Guided Extraction (EDGE) method was compared.
- •ASE and EDGE methods were used to extract pesticides from citrus and alfalfa leaves.
- •The ASE and EDGE instruments had comparable extraction efficiency.
- •The EDGE instrument extracted samples ~4.5 times faster than the ASE instrument.
| Für die chromatographische Analytik (GC/HPLC) und die gravimetrische Messung von Analyten bzw. Summenparametern ist häufig eine Lösemittelextraktion vorgeschaltet. Traditionell dauert die Soxhlet-Extraktion viele Stunden und benötigt eine große Lösemittelmenge. Im Rahmen dieses Online-Seminars erläutern Ihnen die Referenten Frank Scholten und Ulf Sengutta die modernen Lösemittel-Extraktionen von wenigen Milligramm Einwaage bis hin zu mehreren Gramm Einwaage u. a. mit folgenden Themen:
In praktischen Übungen werden live Proben bearbeitet. Und zudem können per Chat individuelle Fragen gestellt werden. Es besteht die Möglichkeit der Bearbeitung von Kundenproben nach dem Online-Seminar.
|
Lösemittel-Extraktionen im MARS und EDGE
Soils and river sediments were frozen and freezedried at ETH Zürich. Soils were sieved, and the fraction <2 mm was used for further analysis. Analytical techniques for brGDGT analyses follow Hopmans et al. (2016) and Freymond et al. (2017) and are summarized here with a detailed description in the supporting information. Briey, between 2 and 3 g of the soil samples and around 20 g of the river sediments were
extracted with solvents in a microwave or an automated extraction system. After purification via column chromatography and preltration, the GDGT distributions were analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (HPLC MS) at ETH Zürich.