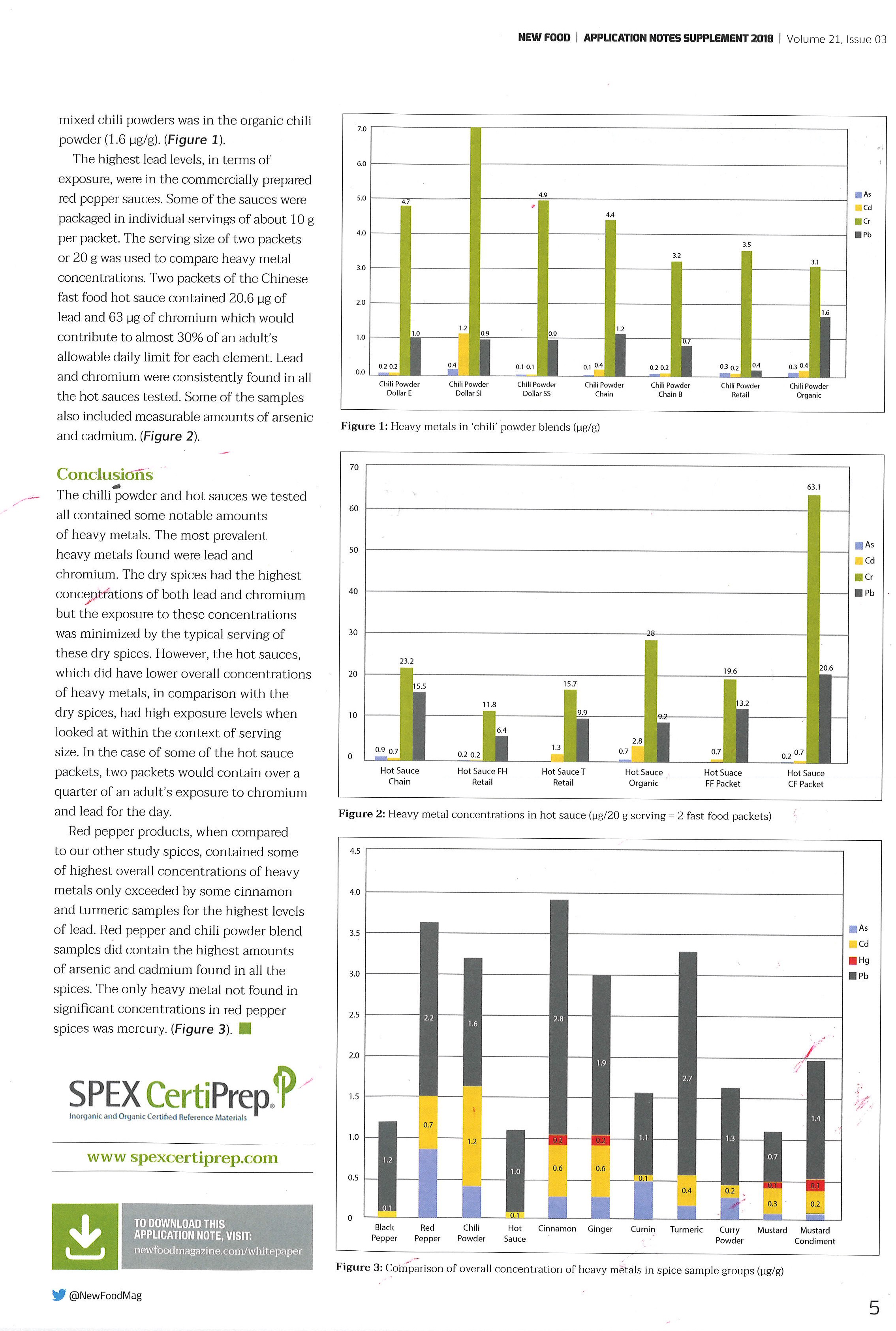
Tag: Mars 5
Lösemittel-Extraktionen im MARS und EDGE
Soils and river sediments were frozen and freezedried at ETH Zürich. Soils were sieved, and the fraction <2 mm was used for further analysis. Analytical techniques for brGDGT analyses follow Hopmans et al. (2016) and Freymond et al. (2017) and are summarized here with a detailed description in the supporting information. Briey, between 2 and 3 g of the soil samples and around 20 g of the river sediments were
extracted with solvents in a microwave or an automated extraction system. After purification via column chromatography and preltration, the GDGT distributions were analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (HPLC MS) at ETH Zürich.
Extraktion mit dem MARS und EDGE:
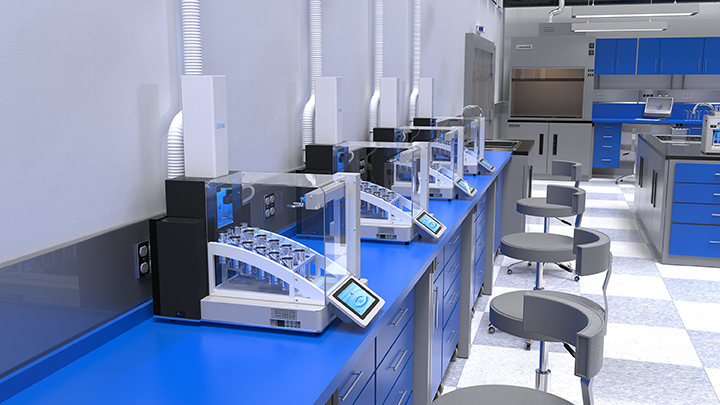
Lipids were extracted from dried soil samples using a microwave (CEM MARS5) or an Energized Dispersive Guided Extraction (CEM EDGE) system. No difference in performance was observed for the different extraction systems. Samples were processed in batches of roughly 15 to 20 g of material. For microwave extraction the samples were transferred to the extraction vessels and covered by a dichloromethane (DCM):methanol (MeOH) 9:1 (v/v, 25 ml) solvent mixture. Extraction temperature was programmed to ramp to 100 ◦C in 35 min and is subsequently held for 20 min. For EDGE extraction 25 ml DCM:MeOH 9:1105 (v/v) was used for extraction at 110 ◦C for 2 min and subsequent rinsing with 15 ml followed by a second extraction with 5 ml of solvent at100 ◦C and rinsing with35ml. The process was repeated on additional samplebatches to yield sufficient quantities of the target lipid compounds for 14C analysis. Pooled extracts were then dried under nitrogen flow.